The Inhibitory Effect of Some Types of Apple Cider Vinegar on Pseudomonas aeruginosa Isolated from Surgical Wounds
Keywords:
Pseudomonas aeruginosa, natural apple cider vinegar, synthetic apple cider vinegarAbstract
Apple cider vinegar (ACV) is primarily produced from apples and contains several antioxidants such as catechin, epicatechin, gallic, caffeic, and chlorogenic acids, which act against harmful free radicals responsible for oxidative stress in the body, thereby maintaining overall human health. It also promotes heart health through various mechanisms and helps reduce cholesterol levels. Moreover, due to its antibiotic properties, it can treat bacterial infections.
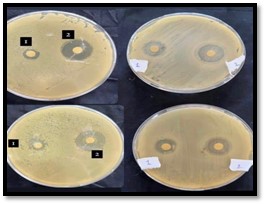
In this study, the inhibitory effect of apple cider vinegar was tested against Pseudomonas aeruginosa, a bacterium isolated and identified through Gram staining and biochemical tests, including the catalase test and oxidase test, as well as an antibiotic susceptibility test. The bacterial strains were isolated from post-surgical wound infections at Misurata Hospital, confirmed, and subjected to biochemical and inhibitory activity analyses using both natural (Libyan) and synthetic (Turkish) apple cider vinegars.
The results showed differences in the acetic acid concentration between the natural and synthetic vinegars, with the latter exhibiting a higher concentration. Similarly, there was a variation in pH values between the two types at the same temperature, where the synthetic vinegar had a higher pH. The findings revealed that apple cider vinegar has a noticeable inhibitory effect on Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from surgical wounds, and that the inhibitory efficiency increases proportionally with the acetic acid concentration..
Downloads